electric field on ddipoles with a box Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): The net electric field is the vector sum of the field of the dipole plus the external field. Recall that we found the electric field of a dipole. If we rewrite it in terms of the dipole moment we get: \[\vec{E}(z) = \dfrac{1}{4 \pi . zline 30 in. ducted under cabinet range hood in stainless steel - hardwired power (615-30)
0 · symbol for electric dipole moment
1 · permanent electric dipole moment
2 · how to calculate dipole moment
3 · electric field perpendicular to dipole
4 · electric field due to dipole at axial point
5 · electric field due to dipole at any point
6 · electric field at axial point of dipole
7 · calculate electric field of dipole
This pedal has two effects in one box, a clean boost and a distortion circuit. This Box of Rock simulates Zachary’s favorite amp turned up all the way, a 1966 Marshall® JTM45. The tone control adjusts brightness and there’s a high-headroom low-noise boost.
Arrange positive and negative charges in space and view the resulting electric field and electrostatic potential. Plot equipotential lines and discover their relationship to the electric field. Create models of dipoles, capacitors, and more!What are the stable orientation(s) for a dipole in an external electric field? What happens if the dipole is slightly perturbed from these orientations?
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): The net electric field is the vector sum of the field of the dipole plus the external field. Recall that we found the electric field of a dipole. If we rewrite it in terms of the dipole moment we get: \[\vec{E}(z) = \dfrac{1}{4 \pi .Figure 5.33 A dipole is induced in a neutral atom by an external electric field. The induced dipole moment is aligned with the external field.In these notes, I write down the electric field of a dipole, and also the net force and the torque on a dipole in the electric field of other charges. For simplicity, I focus on ideal dipoles — also .
Rotation of a Dipole due to an Electric Field. In example \(\PageIndex{1B}\) we discussed, and calculated, the electric field of a dipole: two equal and opposite charges that are “close” to each other.If we want the electric field of the dipole we can get it by taking the gradient of $\phi$. For example, the $z$-component of the field is $-\ddpl{\phi}{z}$.An electric dipole is defined as a couple of opposite charges q and –q separated by a distance d. By default, the direction of electric dipole in space is always from negative charge -q to positive charge q. The midpoint q and –q is called the .
Electric Dipole Field Components of the electric eld are derived from E= r V In spherical polar coordinates: Er = @V @r = 2pcos 4ˇ 0r3 E = 1 r @V @ = psin 4ˇ 0r3 In cartesian coordinates, .Arrange positive and negative charges in space and view the resulting electric field and electrostatic potential. Plot equipotential lines and discover their relationship to the electric field. Create models of dipoles, capacitors, and more!Multiplying the forces by the moment arms, and summing, we find that the magnitude of the torque on this dipole is: τ = 2[qEd 2sinθ] = qd E sinθ. The magnitude of the dipole moment appears in the equation, as does the strength of the electric field, .
What are the stable orientation(s) for a dipole in an external electric field? What happens if the dipole is slightly perturbed from these orientations?

symbol for electric dipole moment
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): The net electric field is the vector sum of the field of the dipole plus the external field. Recall that we found the electric field of a dipole. If we rewrite it in terms of the dipole moment we get: \[\vec{E}(z) = \dfrac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_0} \dfrac{\vec{p}}{z^3}.\]Figure 5.33 A dipole is induced in a neutral atom by an external electric field. The induced dipole moment is aligned with the external field.In these notes, I write down the electric field of a dipole, and also the net force and the torque on a dipole in the electric field of other charges. For simplicity, I focus on ideal dipoles — also called pure dipoles — where the distance a between the positive and the negative Rotation of a Dipole due to an Electric Field. In example \(\PageIndex{1B}\) we discussed, and calculated, the electric field of a dipole: two equal and opposite charges that are “close” to each other.
If we want the electric field of the dipole we can get it by taking the gradient of $\phi$. For example, the $z$-component of the field is $-\ddpl{\phi}{z}$.An electric dipole is defined as a couple of opposite charges q and –q separated by a distance d. By default, the direction of electric dipole in space is always from negative charge -q to positive charge q. The midpoint q and –q is called the centre of the dipole.
Electric Dipole Field Components of the electric eld are derived from E= r V In spherical polar coordinates: Er = @V @r = 2pcos 4ˇ 0r3 E = 1 r @V @ = psin 4ˇ 0r3 In cartesian coordinates, where the dipole axis is along z: Ez = p(3cos2 1) 4ˇ 0r3 Ex=y = 3pcos sin 4ˇ 0r3 Electric dipole eld decreases like 1=r3 (for r ˛ a) 3
Arrange positive and negative charges in space and view the resulting electric field and electrostatic potential. Plot equipotential lines and discover their relationship to the electric field. Create models of dipoles, capacitors, and more!Multiplying the forces by the moment arms, and summing, we find that the magnitude of the torque on this dipole is: τ = 2[qEd 2sinθ] = qd E sinθ. The magnitude of the dipole moment appears in the equation, as does the strength of the electric field, .What are the stable orientation(s) for a dipole in an external electric field? What happens if the dipole is slightly perturbed from these orientations?Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): The net electric field is the vector sum of the field of the dipole plus the external field. Recall that we found the electric field of a dipole. If we rewrite it in terms of the dipole moment we get: \[\vec{E}(z) = \dfrac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_0} \dfrac{\vec{p}}{z^3}.\]
Figure 5.33 A dipole is induced in a neutral atom by an external electric field. The induced dipole moment is aligned with the external field.In these notes, I write down the electric field of a dipole, and also the net force and the torque on a dipole in the electric field of other charges. For simplicity, I focus on ideal dipoles — also called pure dipoles — where the distance a between the positive and the negative Rotation of a Dipole due to an Electric Field. In example \(\PageIndex{1B}\) we discussed, and calculated, the electric field of a dipole: two equal and opposite charges that are “close” to each other.If we want the electric field of the dipole we can get it by taking the gradient of $\phi$. For example, the $z$-component of the field is $-\ddpl{\phi}{z}$.
An electric dipole is defined as a couple of opposite charges q and –q separated by a distance d. By default, the direction of electric dipole in space is always from negative charge -q to positive charge q. The midpoint q and –q is called the centre of the dipole.
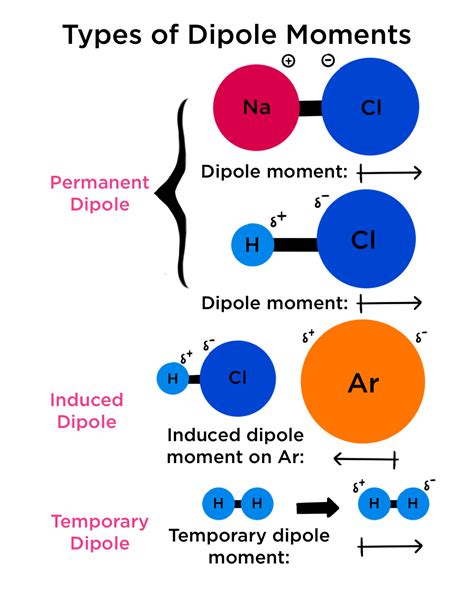
permanent electric dipole moment
It uses an EF86 pentode in triode configuration, which produces primarily odd-order harmonics, instead of the even-order harmonics produced by a 12AX7 or any other triode.
electric field on ddipoles with a box|calculate electric field of dipole